NetbiosX - Windows PrivEscal - Kernel Exploits
Windows Kernel Exploits
Windows by default are vulnerable to several vulnerabilities that could allow an attacker to execute malicious code in order to abuse a system. From the other side patching systems sufficiently is one of the main problems in security. Even if an organization has a patching policy in place if important patches are not implemented immediately this can still give short window to an attacker to exploit a vulnerability and escalate his privileges inside a system and therefore inside the network.
This article will discuss how to identify missing patches related to privilege escalation and the necessary code to exploit the issue.
Discovery of Missing Patches
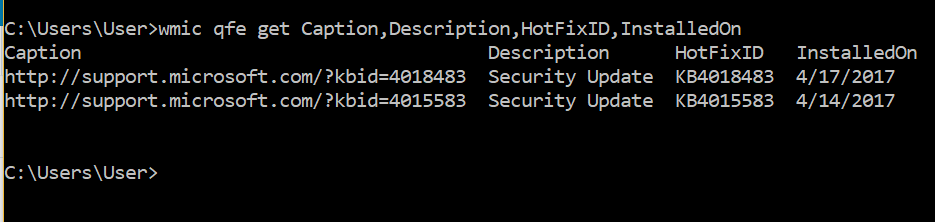
The discovery of missing patches can be identified easily either through manual methods or automatic. Manually this can be done easily be executing the following command which will enumerate all the installed patches.
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn
The output will be similar to this:
The HotFixID can be used in correlation with the table below in order to discover any missing patches related to privilege escalation. As the focus is on privilege escalation the command can be modified slightly to discover patches based on the KB number.
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn | findstr /C:"KB3136041" /C:"KB4018483"
Alternatively this can be done automatically via Metasploit, Credential Nessus Scan or via a custom script that will look for missing patches related to privilege escalation.
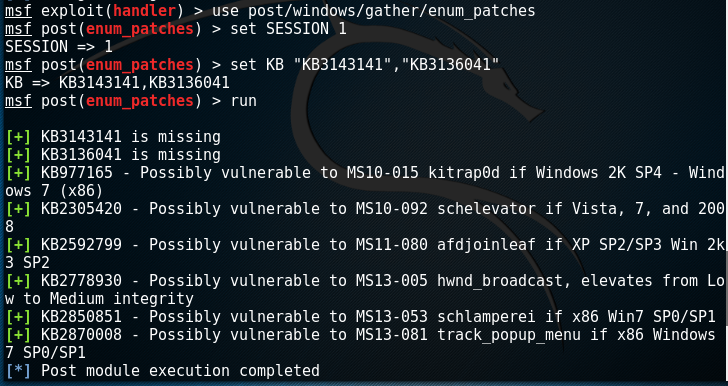
Metasploit
There is a Metasploit module which can quickly identify any missing patches based on the Knowledge Base number and specifically patches for which there is a Metasploit module.

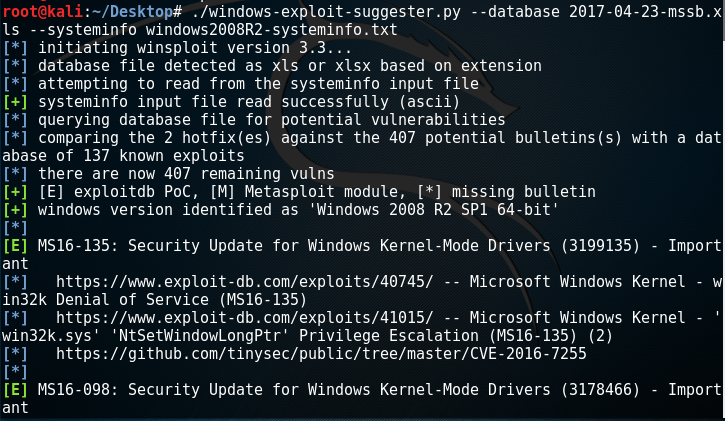
Windows Exploit Suggester
Gotham Digital Security released a tool with the name Windows Exploit Suggester which compares the patch level of a system against the Microsoft vulnerability database and can be used to identify those exploits that could lead to privilege escalation. The only requirement is that requires the system information from the target.
PowerShell
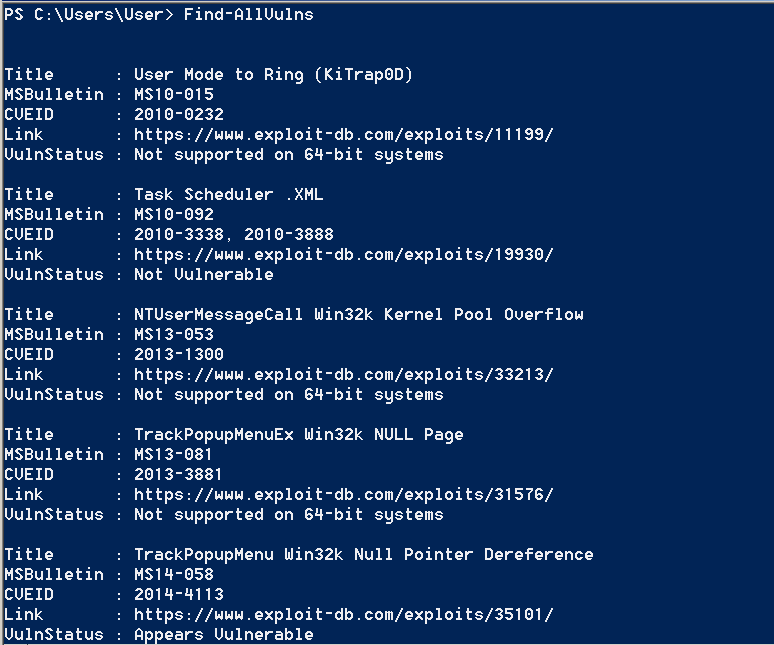
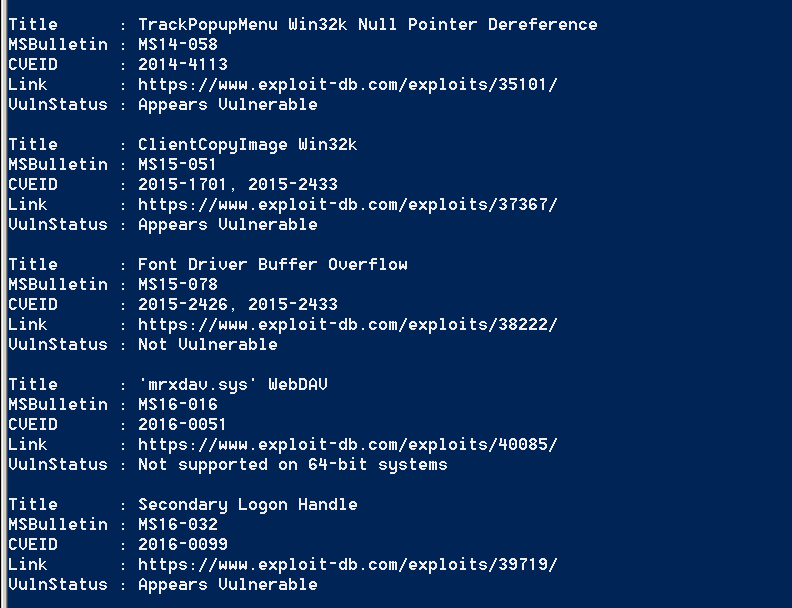
There is also a PowerShell script which target to identify patches that can lead to privilege escalation. This script is called Sherlock and it will check a system for the following:
- MS10-015 : User Mode to Ring (KiTrap0D)
- MS10-092 : Task Scheduler
- MS13-053 : NTUserMessageCall Win32k Kernel Pool Overflow
- MS13-081 : TrackPopupMenuEx Win32k NULL Page
- MS14-058 : TrackPopupMenu Win32k Null Pointer Dereference
- MS15-051 : ClientCopyImage Win32k
- MS15-078 : Font Driver Buffer Overflow
- MS16-016 : ‘mrxdav.sys’ WebDAV
- MS16-032 : Secondary Logon Handle
- CVE-2017-7199 : Nessus Agent 6.6.2 – 6.10.3 Priv Esc
The output of this tool can be seen below:
Privilege Escalation Table
The following table has been compiled to assist in the process of privilege escalation due to lack of sufficient patching.
Recent Posts
Tags
Categories
Active directory Burpsuite Cheatsheet Crackmapexec Empire Events Exploit File transfer Iis Implants Kcsec Kerberos Kernelpop Ksec Ksec snapshot Lab Metasploit Metasploitable Msfvenom Netcat Nfc & rfid Nikto Nmap Pivoting Privilege escalation Proxmark Proxychains Redteam Responder Rubber ducky Shells Sqlmap Sshutle Thefatrat Toolkit Webapp Windows domain Xss